
Most melanomas are found by patients or their partners – not by medical providers.
60% You know your skin best – checking your skin and talking to a medical provider if you find something suspicious is shown in research studies to increase the likelihood of survival.
Most people have moles and other lesions (abnormal spots, bumps, or sores) on their skin, and the vast majority of these are harmless.
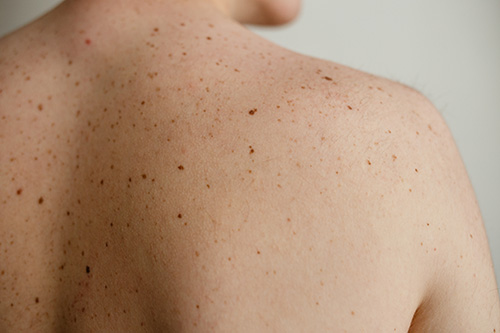
A key indicator for a concerning mole is a change in appearance — primarily size, shape and coloration.
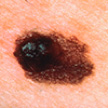
Irregular shape (“funny looking”)
One side looks different
Growing differently
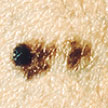
Irregular color (compare it with your other moles)
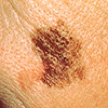
The size is changing
As we age, moles may gradually and subtly change in appearance, but a mole should never change quickly (within a few weeks or months). To be on the safe side, any changing mole should be evaluated by a medical provider.
Skin cancer (melanoma or other skin cancers) appears on the body in many different ways. It can look like a:
- Changing mole — as earlier discussed, this is one of the most important indicators of melanoma
- New mole (this is normal in younger people, but new moles are not normal later in life)
- Mole that “stands out” or looks different from the others
Make an Appointment
OHSU Department of Dermatology offers several care options, including:
In-person appointments Video appointments Telephone appointments Email appointments
For all of your scheduling needs, please call: 503-418-3376.
Melanoma
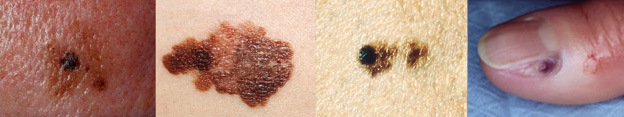
Melanoma is the most dangerous form of skin cancer, which develop when pigment-producing cells (melanocytes) mutate and become cancerous.
- Melanoma often arises as a new growth on the skin,
- or a change in an existing mole.
Common signs of a melanoma include asymmetry, uneven borders, having a variety of colors, being larger than 6mm in diameter and/or a mole that’s evolved over time. You can remember with the ABCDE guide:

Asymmetry: One side is not like the other.
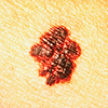
Border: The edges are irregular or ragged.
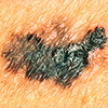
Color: It has color variations, such as shades of brown or black, sometimes with patches of pink, red or white.

Diameter: It’s more than 6 millimeters across (the size of a pencil eraser), though it can be smaller.

Evolving: The mole may change in size, color or shape.
Melanoma can occur anywhere on the body, even places that are usually covered by clothes and not exposed to the sun.
Melanoma can start small, and grow larger, but it can also grow deeper into the skin, where it can become much more dangerous:
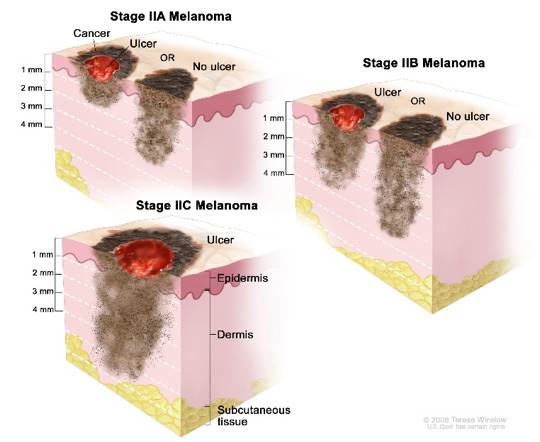
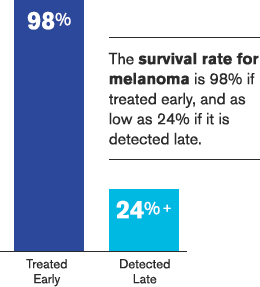
98% chance of survival when melanoma is treated at an early stage. This can decrease to as low as a 24% chance of survival with late stage melanoma that has spread.
Source: National Cancer Institute
Learn More: Skin Cancer Foundation – Skin Cancer Facts & Statistics
Non-cancerous skin lesions
Moles
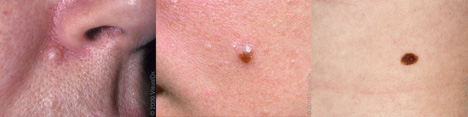
Moles have well-defined borders, can be raised or flat, can be brown or skin-colored, and usually don’t change color with sun exposure. Moles are mostly round or oval shaped — occasionally they can be odd shaped or atypical. Learn more.
Freckles
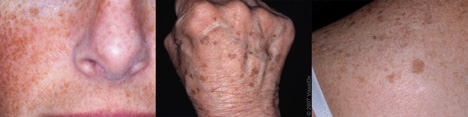
Freckles are flat, light brown spots with lacey borders. They appear most often on parts of the body commonly exposed to the sun. Learn more.
Sebhorrheic Keratosis (SK)
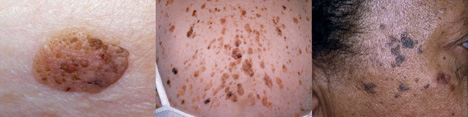
Sebhorrheic Keratosis are crusty, brown growths that look “stuck on”. These are very common in adults ages 60 or older. These at times may resemble a type of skin cancer, but are not premalignant tumors. Learn more.
If you have any questions – always ask your doctor.
Other Types of Skin Cancer (Non-melanoma)
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC)
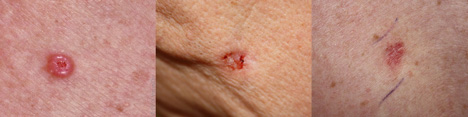
Basal Cell Carcinomas are cancerous growths or sores that appear on highly-exposed areas like the scalp, face, neck and back of hands. They can appear as a flesh colored or translucent bump, with rolled borders, that may rupture, bleed and scab. They can also present as a dark lesion — black, blue, brown, or a slightly scaly patch that grow over time. Basal Cell Carcinoma is the most common skin cancer. Learn more.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC)
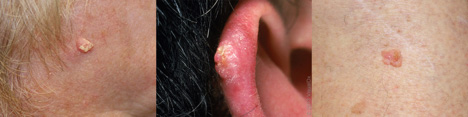
Squamous Cell Carcinomas are cancerous growths that present as enlarging lumps or sores that are crusted or scaly. These are found most commonly in highly-exposed areas of the body. Learn more.
Actinic Keratosis (AK)
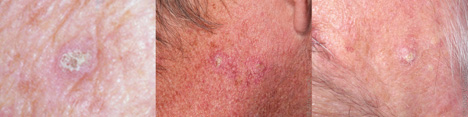
Actinic Keratoses are rough, scaly cancerous growths caused by sun damage. They are most commonly found on areas of the body that are highly-exposed to the sun, like the face, ears, scalp, neck and arms. Learn more.
What causes skin cancer and melanoma?
While you look — MoleMapper™ can help you track your moles.
Take control of your skin health — from the palm of your hand.
Available on the App Store, MoleMapper™ is an iPhone app designed to help you map, measure and monitor your moles over time.
One of the most important warning signs of melanoma is a change in the skin, but it can be difficult to remember what our skin lesions (moles, freckles, etc…) look like from month to month. MoleMapper™ uses your cellphone camera to capture images of your skin lesions, allows you to map them, measure their size in reference to a common object like a coin, and then compare them to past images to monitor for changes. Learn more.

